버튼에 기능 부여하는 법
FloatingActionButton() → 버튼에 기능 넣기
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
var a = 1;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
child: Text(a.toString()),
onPressed: () {
setState(() {
a++;
});
},
),
appBar: AppBar(),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: 3,
itemBuilder: (c, i) {
return ListTile(
leading: Icon(Icons.account_circle_rounded),
title: Text('홍길동'),
);
},
)
)
);
}
}기능을 넣을 때 계속 변하는 값을 넣으려는 경우 → state 사용
- 자료를 잠시 저장하는 곳 : 변수 or state
- 변수는 자동으로 재렌더링이 안됨
- state는 자동으로 재렌더링이 됨
- state 생성 방법
- 첫 번째 방법 : stful 입력 후 탭 키
class 클래스 명 extends StatefulWidget { const Test({Key? key}) : super(key: key); @override State<Test> createState() => _TestState(); } class _TestState extends State<Test> { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return const Placeholder(); } }
- 두 번째 방법 : `class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {이 부분에서StatelessWidget을 클릭 후 전구 모양 아이콘 클릭하면StatefulWidget` 으로 변경할 수 있음
- state 변경은 무조건 setState 함수로 해야한다.
MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
floatingActionButtion: FloatingActionButton(
child : Text(a.toString()),
onPressed: (){
setState((){
a++
});
}
),
appBar: AppBar(),
body: 생략
),
)예제 1
연락처 앱과 같이 이름이 변경되도록 하는 방법
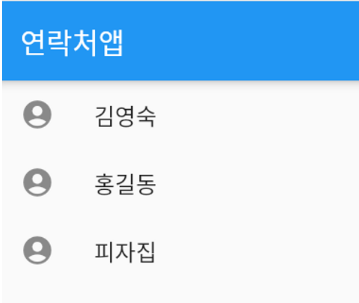
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
var a = 1;
var name = ['김영숙', '홍길동', '피자집'];
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar( title: Text('연락처앱')),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: 3,
itemBuilder: (c, i) {
return ListTile(
leading: Icon(Icons.account_circle_rounded),
title: Text(name[i]),
);
},
)
)
);
}
}예제 2
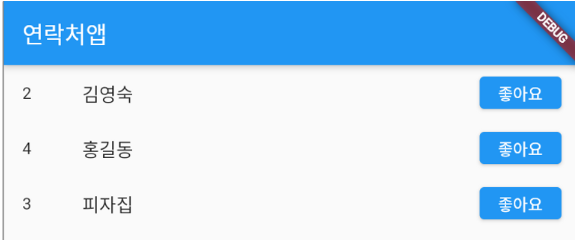
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
var like = [0, 0, 0];
var name = ['김영숙', '홍길동', '피자집'];
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar( title: Text('연락처앱')),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: 3,
itemBuilder: (c, i) {
return ListTile(
leading: Text(like[i].toString()),
title: Text(name[i]),
trailing: ElevatedButton(
child: Text('좋아요'),
onPressed: () {
setState(() {
like[i]++;
});
},
),
);
},
)
)
);
}
}버튼 클릭 시 Dialog 생성 방법
showDialog() 함수를 사용하면 Dialog 사용 가능
FloatingActionButton(
child: Text('버튼'),
onPressed: () {
showDialog(
context: context,
builder: (context){
return Dialog(
child: Text('AlertDialog Title'),
);
},
);
},
),⇒ 근데 Dialog가 안나옴 → MaterialApp()을 MyApp 클래스에서 빼줘야 Dialog가 동작함
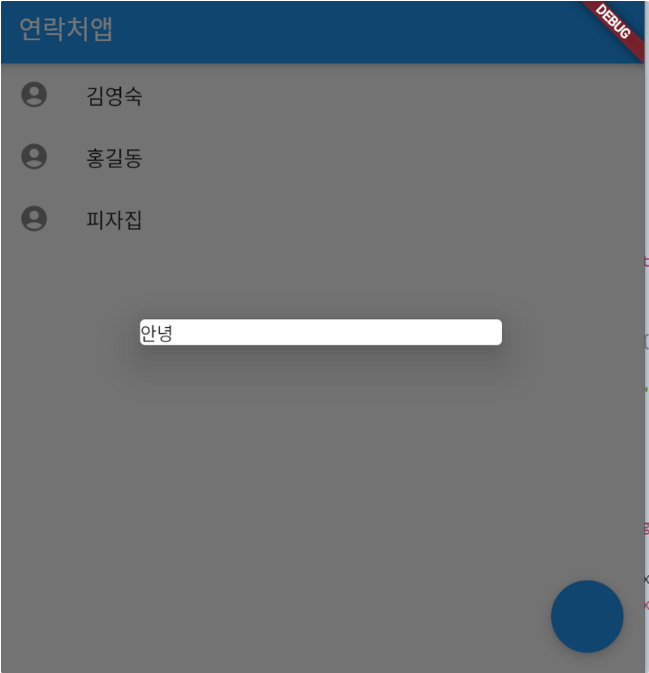
void main() {
runApp(
MaterialApp(
home: MyApp()
)
);
}
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
MyApp({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
State<MyApp> createState() => _MyAppState();
}
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
var like = [0, 0, 0];
var name = ['김영숙', '홍길동', '피자집'];
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
showDialog(context: context, builder: (context) {
return Dialog(child: Text('안녕'));
});
},
),
appBar: AppBar( title: Text('연락처앱')),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: 3,
itemBuilder: (c, i) {
return ListTile(
leading: Icon(Icons.account_circle_rounded),
title: Text(name[i]),
);
},
)
);
}
}
context란?
class 위젯명 extends StatelessWidget {
@override
build (context) {
어쩌구 생략- 커스텀 위젯 만들 때 보면 build() 함수를 쓰도록 되어있다.
- build() 함수안에 첫 파라미터 넣으시면 그건 무조건 현재 위젯의 부모들이 누군지 담겨있다.
- 쉽게 비유하자면 족보다.
- context도 내 아빠 위젯, 할배 위젯, 증조할배 위젯이 누구인가 알려주는 족보다.
💡 Q. class 커스텀위젯안에 있는 context에는 뭐가 담겨있나?
- 커스텀위젯의 모든 조상들의 정보를 담고있으니 MaterialApp, Scaffold 이런 것들이 담겨있다.
💡 Q. 그럼 class MyApp 안에 있는 context는 뭐가 담겨있나?
- MyApp 위젯의 모든 조상들에 대한 정보를 담고 있는 변수다.
- 부모가 없기 때문에 그래서 들어있는 게 아무것도 없다.
Flutter 함수들
- showDialog()
- Navigator()
- Theme.of()
- Scaffold.of()
⇒ 이런 함수들은 context를 (족보를) 소괄호 안에 집어넣어야 잘 작동하는 함수다.
→ 이 중에서 showDialog() 함수는 족보를 넣는데 족보 중에 MaterialApp이 들어있어야 제대로 작동한다.
showDialog( context : MaterialApp이부모로들어있는족보 )- 사용방법
- 첫 번째 방법 : MaterialApp을 따로 빼줘야 함
// 이건 context가 가져오는 정보가 없음 -> MaterialApp을 따로 빼줘야 함 build (context) { return MaterialApp( home: Scaffold( floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton( onPressed: (){ showDialog( context: context, builder: (context){ return Dialog( child: Text('안녕'), ); }, ); }, ), // 이렇게 해야 됨 void main() { runApp( MaterialApp( // <- 여기로 빼주기 home: MyApp() ) ); } class MyApp extends StatefulWidget { MyApp({Key? key}) : super(key: key); @override State<MyApp> createState() => _MyAppState(); } class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> { var like = [0, 0, 0]; var name = ['김영숙', '홍길동', '피자집']; @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton( onPressed: () { showDialog(context: context, builder: (context) { return Dialog(child: Text('안녕')); }); }, ), appBar: AppBar( title: Text('연락처앱')), body: ListView.builder( itemCount: 3, itemBuilder: (c, i) { return ListTile( leading: Icon(Icons.account_circle_rounded), title: Text(name[i]), ); }, ) ); } } - 두 번째 방법 : 족보를 하나 더 만들기
build (context) { return MaterialApp( home: Scaffold( floatingActionButton: Builder( builder: (jokbo1) { return FloatingActionButton( onPressed: (){ showDialog( context: jokbo1, builder: (context){ return Dialog( child: Text('AlertDialog Title'), ); }, ); }, ); } ),- jokbo1은 Scaffold, MaterialApp이 들어있는 족보가 되기 때문에 아까의 문제가 해결된다.
- 이런 건 직접 짜는게 아니라 원하는 위젯 하나에 커서 찍고 왼쪽 전구 누르시면 Builder로 감싸기 쓰면 된다.
- 그러나 해결책 2는 치우고 해결책 1 쓰는게 좋음
- Builder() 이건 복잡해지니 귀찮다. 응급상황에 써라.
- 첫 번째 방법 : MaterialApp을 따로 빼줘야 함
예제
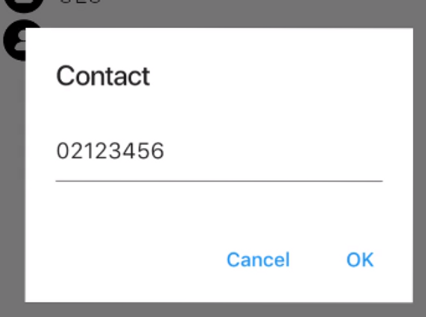
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(
MaterialApp(
home: MyApp()
)
);
}
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
MyApp({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
State<MyApp> createState() => _MyAppState();
}
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
var a = 3;
var like = [0, 0, 0];
var name = ['김영숙', '홍길동', '피자집'];
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
showDialog(context: context, builder: (context) {
return DialogUI();
});
},
),
appBar: AppBar( title: Text('연락처앱')),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: 3,
itemBuilder: (c, i) {
return ListTile(
leading: Icon(Icons.account_circle_rounded),
title: Text(name[i]),
);
},
)
);
}
}
class DialogUI extends StatelessWidget {
const DialogUI({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Dialog(
child: SizedBox(
width: 300,
height: 300,
child: Column(
children: [
TextField(),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
children: [
TextButton(child: Text('취소'), onPressed: (){ Navigator.pop(context);}),
TextButton(child: Text('완료'), onPressed: () {})
],
)
],
),
)
);
}
}자식 위젯이 부모 위젯의 state를 쓰고 싶다면?
- 부모 → 자식 state를 전송하면 됨
// 1. 보내려면 자식위젯(작명 : 보낼 state)
DialogUI(state: a);
// 2. 받아온 변수를 등록해야한다 (두 곳에)
class DialogUI extends StatelessWidget {
const DialogUI({Key? key, this.state}) : super(key: key);
final state; // final이 아닌 var를 쓰고 싶다면 윗 줄에 const를 제거하면 됨import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(
MaterialApp(
home: MyApp()
)
);
}
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
MyApp({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
State<MyApp> createState() => _MyAppState();
}
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
var a = 3;
var like = [0, 0, 0];
var name = ['김영숙', '홍길동', '피자집'];
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
showDialog(context: context, builder: (context) {
return DialogUI(state: a);
});
},
),
appBar: AppBar( title: Text('연락처앱')),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: 3,
itemBuilder: (c, i) {
return ListTile(
leading: Icon(Icons.account_circle_rounded),
title: Text(name[i]),
);
},
)
);
}
}
class DialogUI extends StatelessWidget {
const DialogUI({Key? key, this.state}) : super(key: key);
final state;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Dialog(
child: SizedBox(
width: 300,
height: 300,
child: Column(
children: [
TextField(),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
children: [
TextButton(child: Text(state.toString()), onPressed: (){ Navigator.pop(context);}),
TextButton(child: Text('완료'), onPressed: () {})
],
)
],
),
)
);
}
}자식 위젯이 부모 위젯의 state를 변경하고 싶으면?
// 1. 부모에 수정함수 생성
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
var name = ['김영숙', '홍길동', '피자집'];
var total = 3;
addOne() {
setState(() {
total++;
});
}
// 2. 자식 위젯에 함수 전송
(MyApp 안의 DialogUI() 쓰던 곳)
DialogUI( addOne : addOne )
// 3. 자식 위젯에 파라미터 등록
class DialogUI extends StatelessWidget {
DialogUI({Key? key, this.addOne }) : super(key: key);
final addOne;
// 4. 함수 사용
(DialogUI위젯 내부)
TextButton(
child: Text('완료'),
onPressed: (){
addOne();
},
),
// 전체 코드
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(
MaterialApp(
home: MyApp()
)
);
}
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
MyApp({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
State<MyApp> createState() => _MyAppState();
}
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
var total = 3;
var like = [0, 0, 0];
var name = ['김영숙', '홍길동', '피자집'];
addOne() {
setState(() {
total++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
showDialog(context: context, builder: (context) {
return DialogUI(addOne: addOne);
});
},
),
appBar: AppBar( title: Text(total.toString())),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: 3,
itemBuilder: (c, i) {
return ListTile(
leading: Icon(Icons.account_circle_rounded),
title: Text(name[i]),
);
},
)
);
}
}
class DialogUI extends StatelessWidget {
const DialogUI({Key? key, this.addOne}) : super(key: key);
final addOne;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Dialog(
child: SizedBox(
width: 300,
height: 300,
child: Column(
children: [
TextField(),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
children: [
TextButton(child: Text('취소'), onPressed: (){ Navigator.pop(context);}),
TextButton(child: Text('완료'), onPressed: () {addOne(); })
],
)
],
),
)
);
}
}사용자의 input 받는 법
// 1. TextEditingController()를 담을 변수 생성하기
class DialogUI extends StatelessWidget {
DialogUI({Key? key, this.addOne }) : super(key: key);
final addOne;
var inputData = TextEditingController();
// 2. TextField() 위젯에 controller: 파라미터가 있는데 거기에 변수 삽입
TextField(
controller: inputData,
),
// 전체 코드
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(
MaterialApp(
home: MyApp()
)
);
}
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
MyApp({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
State<MyApp> createState() => _MyAppState();
}
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
var total = 3;
var like = [0, 0, 0];
var name = ['김영숙', '홍길동', '피자집'];
addOne() {
setState(() {
total++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
showDialog(context: context, builder: (context) {
return DialogUI(addOne: addOne);
});
},
),
appBar: AppBar( title: Text(total.toString())),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: 3,
itemBuilder: (c, i) {
return ListTile(
leading: Icon(Icons.account_circle_rounded),
title: Text(name[i]),
);
},
)
);
}
}
class DialogUI extends StatelessWidget {
DialogUI({Key? key, this.addOne}) : super(key: key);
final addOne;
var inputData = TextEditingController();
var inputData2 = '';
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Dialog(
child: SizedBox(
width: 300,
height: 300,
child: Column(
children: [
TextField(controller: inputData),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
children: [
TextButton(child: Text('취소'), onPressed: (){ Navigator.pop(context);}),
TextButton(child: Text('완료'), onPressed: () {addOne(); })
],
)
],
),
)
);
}
}
입력된 값을 ListView에 추가하기
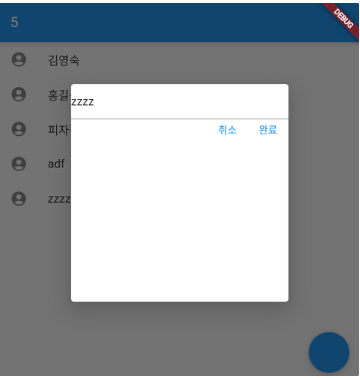
addName(a) {
setState(() {
name.add(a);
});
}
// 2. 자식 위젯에 함수 전송
DialogUI(addOne: addOne, addName : addName );
// 3. 자식 위젯에 파라미터로 받기
class DialogUI extends StatelessWidget {
DialogUI({Key? key, this.addOne, this.addName}) : super(key: key);
final addOne, addName;
// 4. 함수 사용
// -> 부모 위젯의 ListView 길이가 고정되어있으면 이렇게(itemCount: name.length) 변경해야 함
TextButton(
child: Text('완료'),
onPressed: () {
addOne();
addName(inputData.text);
})
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(
MaterialApp(
home: MyApp()
)
);
}
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
MyApp({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
State<MyApp> createState() => _MyAppState();
}
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
var total = 3;
var like = [0, 0, 0];
var name = ['김영숙', '홍길동', '피자집'];
addName(a) {
setState(() {
name.add(a);
});
}
addOne() {
setState(() {
total++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
showDialog(context: context, builder: (context) {
return DialogUI(addOne: addOne, addName : addName );
});
},
),
appBar: AppBar( title: Text(total.toString())),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: name.length,
itemBuilder: (c, i) {
return ListTile(
leading: Icon(Icons.account_circle_rounded),
title: Text(name[i]),
);
},
)
);
}
}
class DialogUI extends StatelessWidget {
DialogUI({Key? key, this.addOne, this.addName}) : super(key: key);
final addOne, addName;
var inputData = TextEditingController();
var inputData2 = '';
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Dialog(
child: SizedBox(
width: 300,
height: 300,
child: Column(
children: [
TextField(controller: inputData),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
children: [
TextButton(child: Text('취소'), onPressed: (){ Navigator.pop(context);}),
TextButton(
child: Text('완료'),
onPressed: () {
addOne();
addName(inputData.text);
})
],
)
],
),
)
);
}
}'Web & Android > Flutter' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Flutter] 사용자 연락처 불러오기 (0) | 2023.09.12 |
|---|---|
| [Flutter] 권한 팝업 요청 기능 (0) | 2023.09.12 |
| [Flutter] 레이아웃 위젯 (0) | 2023.09.12 |
| [Flutter] Lint 관련 워닝 무시하는 법 (0) | 2023.09.12 |
| [Flutter] 위젯(글자, 아이콘, 네모박스, 버튼) (1) | 2023.09.07 |